In accordance to their usage, gears are made of various types of materials, such as iron-based materials, nonferrous metals, or plastic materials. The strength of gears differs depending on the type of material, heat treatment or quenching applied.
9.1 Types of Gear Materials
Table 9.1 lists mechanical properties and characteristics of gear materials most commonly used.
Table 9.1 Types of Gear Materials
Material : Carbon Steel for Structural Machine Usage
JIS Material No. : S15CK
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 490
Elongation (%) More than : 20
Drawability (%) More than : 50
Hardness HB : 143-235
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Low-carbon steel. High hardness obtained by Carburizing.
Material : Carbon Steel for Structural Machine Usage
JIS Material No. : S45C
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 690
Elongation (%) More than : 17
Drawability (%) More than : 45
Hardness HB : 201-269
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Most commonly used medium-carbon steel. Thermal refined / induction hardened.
Material : Alloy steel for Machine Structural Use
JIS Material No. : SCM435
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 930
Elongation (%) More than : 15
Drawability (%) More than : 50
Hardness HB : 269-331
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Medium-carbon alloy steel (C content: 0.3-0.7%). Thermal refined and induction hardened. High strength (High bending strength / High surface durability). Used in gear manufacturing, except for worm gear.
Material : Alloy steel for Machine Structural Use
JIS Material No. : SCM440
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 980
Elongation (%) More than : 12
Drawability (%) More than : 45
Hardness HB : 285-352
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Medium-carbon alloy steel (C content: 0.3-0.7%). Thermal refined and induction hardened. High strength (High bending strength / High surface durability). Used in gear manufacturing, except for worm wheels.
Material : Alloy steel for Machine Structural Use
JIS Material No. : SNCM439
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 980
Elongation (%) More than : 16
Drawability (%) More than : 45
Hardness HB : 293-352
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Medium-carbon alloy steel (C content: 0.3-0.7%). Thermal refined and induction hardened. High strength (High bending strength / High surface durability). Used in gear manufacturing, except for worm wheels.
Material : Alloy steel for Machine Structural Use
JIS Material No. : SCr415
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 780
Elongation (%) More than : 15
Drawability (%) More than : 40
Hardness HB : 217-302
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Low-carbon Alloy Steel (C content below 0.3%). Surface-hardening treatment applied (Carburizing, Nitriding, Carbo-nitriding, etc.) High strength (Bending strength / Surface durability).
Material : Alloy steel for Machine Structural Use
JIS Material No. : SCM415
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 830
Elongation (%) More than : 16
Drawability (%) More than : 40
Hardness HB : 235-321
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Low-carbon Alloy Steel (C content below 0.3%). Surface-hardening treatment applied (Carburizing, Nitriding, Carbo-nitriding, etc.) High strength (Bending strength / Surface durability).
Material : Alloy steel for Machine Structural Use
JIS Material No. :SNC815
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 980
Elongation (%) More than : 12
Drawability (%) More than : 45
Hardness HB : 285-388
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Low-carbon Alloy Steel (C content below 0.3%). Surface-hardening treatment applied (Carburizing, Nitriding, Carbo-nitriding, etc.) High strength (Bending strength / Surface durability).
Material : Alloy steel for Machine Structural Use
JIS Material No. : SNCM220
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 830
Elongation (%) More than : 17
Drawability (%) More than : 40
Hardness HB : 248-341
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Low-carbon Alloy Steel (C content below 0.3%). Surface-hardening treatment applied (Carburizing, Nitriding, Carbo-nitriding, etc.) High strength (Bending strength / Surface durability).
Material : Alloy steel for Machine Structural Use
JIS Material No. : SNCM420
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 980
Elongation (%) More than : 15
Drawability (%) More than : 40
Hardness HB : 293-375
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Low-carbon Alloy Steel (C content below 0.3%). Surface-hardening treatment applied (Carburizing, Nitriding, Carbo-nitriding, etc.) High strength (Bending strength / Surface durability).
Material :Rolled Steel for General Structures
JIS Material No. : SS400
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 400
Elongation (%) More than : –
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : –
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Low strength. Low cost.
Material :Gray Cast Iron
JIS Material No. : FC200
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 200
Elongation (%) More than : –
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : Less than 223
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Low strength than steel. Suitable for bulk production.
Material : Nodular Graphite Cast Iron
JIS Material No. : FCD500-7
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 500
Elongation (%) More than : 7
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : 150-230
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Ductile Cast Iron with high strength. Used in the manufacturing of large casting gears.
Material : Stainless Steel
JIS Material No. :SUS303
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 520
Elongation (%) More than : 40
Drawability (%) More than : 50
Hardness HB : Less than 187
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Has more machinability than SUS304. Increases seizure resistant.
Material : Stainless Steel
JIS Material No. : SUS304
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 520
Elongation (%) More than : 40
Drawability (%) More than : 60
Hardness HB : Less than 187
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Most commonly used stainless Steel. Used for food processing machines etc.
Material : Stainless Steel
JIS Material No. : SUS316
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 520
Elongation (%) More than : 40
Drawability (%) More than : 60
Hardness HB : Less than 187
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Has corrosion resistance against salty seawater, better than SUS304.
Material : Stainless Steel
JIS Material No. : SUS420J2
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : 540
Elongation (%) More than : 12
Drawability (%) More than : 40
Hardness HB : More than 217
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Martensitic stainless steel, quenching can be applied.
Material : Stainless Steel
JIS Material No. : SUS440C
Tensile Strength N/mm2 More than : –
Elongation (%) More than : –
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : More than 58HRC
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : High hardness can be obtained by quenching. High surface durability.
Material : Nonferrous Metals
JIS Material No. : C3604
Tensile Strength N/mm2 : 335
Elongation (%) More than : –
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : More than 80HV
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Free-Cutting Brass. Used in manufacturing of small gears.
Material : Nonferrous Metals
JIS Material No. : CAC502
Tensile Strength N/mm2 : 295
Elongation (%) More than : 10
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : More than 80
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Phosphor bronze casting. Suitable for worm wheels.
Material : Nonferrous Metals
JIS Material No. : CAC702
Tensile Strength N/mm2 : 540
Elongation (%) More than : 15
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : More than 120
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Aluminum-bronze casting. Used for worm wheels etc.
Material : Engineering Plastics
JIS Material No. : MC901
Tensile Strength N/mm2 : 96
Elongation (%) More than : –
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : 120HRR
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Used for machined gears. Lightweight. Anti-rust.
Material : Engineering Plastics
JIS Material No. : MC602ST
Tensile Strength N/mm2 : 96
Elongation (%) More than : –
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : 120HRR
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Used for machined gears. Lightweight. Anti-rust.
Material : Engineering Plastics
JIS Material No. : M90
Tensile Strength N/mm2 : 62
Elongation (%) More than : –
Drawability (%) More than : –
Hardness HB : 80HRR
Characteristics, heat treatments applied : Used for injection-molded gears. Suitable for bulk production at low cost. Applied for use with light load.
9.2 Heat Treatments
Heat treatment is a process that controls the heating and cooling of a material, performed to obtain required structural properties of metal materials. Heating methods include normalizing, annealing quenching, tempering, and surface hardening.
Heat treatment is performed to enhance the properties of the steel. as the hardness increases by applying successive heat treatments, the gear strength increases along with it; the tooth surface strength also increases drastically. As shown in Table 9.2, heat treatments differ depending on the quantity of carbon (C) contained in the steel.
Table 9.2 Heat Treatments
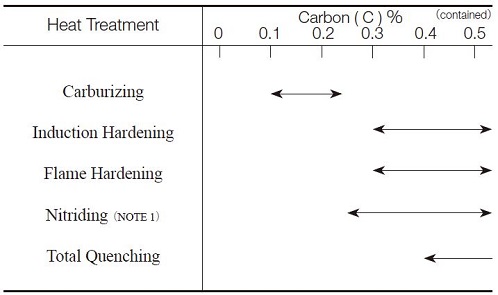
NOTE 1. For nitriding, it is necessary that the material contains one or more alloy elements, such as Al, Cr, Mo. or V.
(1) Normalizing
Normalizing is a heat treatment applied to the microstructure of the small crystals of steel to unify the overall structure. This treatment is performed to relieve internal stress or to resolve inconsistent fiber structure occurred by the forming processing such as rolling.
(2) Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment applied to soften steel, to adjust crystalline structure, to relieve internal stress, and to modify for cold-working and cutting performance. There are several types of annealing in accordance with the application, such as Full Annealing, Softening, Stress Relieving, Straightening Annealing and Intermediate Annealing.
- Full Annealing
Annealing to relieve internal stress without changing the structure. - Straightening Annealing
Annealing to fix deformation occurred in steel, or other materials. The treatment is performed by applying load. - Intermediate Annealing
Annealing applied in the process of cold-working, applied to soften the work-hardened material, so to make the next process easier.
(3) Quenching
Quenching is a treatment on steel, applying rapid cooling after heating at high temperature. There are several types of quenching in accordance with cooling conditions; water quenching, oil quenching, and vacuum quenching. It is essential to apply tempering after quenching.
(4) Tempering
Tempering is a heat treatment, applying cooling at a proper speed. After performing quench hardening, the material is heated again, then, tempering is applied. Tempering must be performed after quenching. Quenching is applied to adjust hardness, to add toughness, and to relieve internal stress. There are two types of tempering, one is high-temperature tempering, and the other is low-temperature tempering. Applying the tempering at higher temperature, the more toughness is obtained, although the hardness decreases.
For thermal refining, high-temperature tempering is performed.
For induction hardening or carburizing, the require tempering performed after surface-hardening treatment is, low-temperature tempering.
(5) Thermal Refining
Thermal Refining is a heat treatment applied to adjust heardness / strength / toughness of steel. This treatment involves quenching and high-temperature tempering, in combination. After thermal refining is performed, the hardness is adjustedby these treatments to increase the metals machinable properties.
The target hadness for thermal refining are :
S45C (Carbon Steel for Machine Structural Use) 200 – 270 HB
SCM440 (Alloy Steel for Machine Structural Use) 230 – 270 HB
(6) Carburizing
Carburizing is a heat treatment performed especially to harden the surface in which carbon is present and penetrates the surface. The surface of low-carbon steel is carburized (Carbon penetration) and in a state of high carbon, where quenching is required. Low-temperature tempering is applied after quenching to adjust the hardness.
Not only the surface, but the inner material structure is also somewhat hardened by some level of carburizing, however, it is not as hard as the surface.
If a masking agent is applied on a part of the surface, carbon penetration is prevented and the hardness is not changed. The target hardness on the surface and the hardened depth are:
– Quench Hardenss 55 – 63 HRC (reference value)
– Effective Hardened Depth 0.3 – 1.2 mm (reference value)
Gears are deformed by carburizing, and the precision is decreased. To improve precision, gear grinding is necessary.
(7) Induction Hardening
Induction Hardening is a heat treatment performed to harden the surface by induction-heating of the steel, composed of 0.3% carbon. For gear products, induction hardening is effective for hardening tooth areas including tooth surface and the tip, however, the root may not be hardened in some cases.
Generally, the precision of gears declines from deformation caused by induction hardening.
For induction hardening of S45C products, please refer to the values below.
– Quench Hardness 45 – 55 HRC
– Effective Hardened Depth 1 – 2 mm
(8) Flame Hardening
Flame Hardening is a surface-hardening treatment performed by flame heating. This treatment is usually performed on the surface for partial hardening of iron and steel.
(9) Nitriding
Nitriding is a heat treatment performed to harden the surface by introducing nitrogen into the surface of steel. If the steel alloy includes aluminum, chrome, and molybdenum, it improves nitriding and the hardness can be obtained. A representative nitride steel is SACM645 (Aluminium chromium molybdenum steel)
(10) Total Quenching
A heat treatment by heating the entire steel material to the core, and then cooling rapidly afterwards, where not only the surface is hardened, the core part is also hardened.
Related links :
齿轮的材料及热处理
Gear Materials and Heat Treatments - A page of The ABC’s of Gears / Basic Guide – B
Materials for Gears and Heat Treatment – A page of Introduction to Gears



