What is a gear module ?
The module (m) is a unit of gear tooth size defined by ISO.
Gears will only mesh with each other if they have teeth of the same module.

Image 1 - A value of module of properly meshing pair of gear is same
(Image shows a pair of gears with module 2)
Pitch (p) represents the distance between teeth, and since a larger pitch means a larger tooth size and a smaller pitch means a smaller tooth size, the pitch can be used to represent the tooth size.
The pitch circle of a gear corresponds to the outer circumference of the friction wheel (gears can be thought of as friction wheels with teeth attached) and is the reference circle for determining the pitch of the gear teeth.
The circumference of the pitch circle (πd) is its diameter (pitch circle diameter = d) multiplied by the pi π. The pitch is obtained by dividing the pitch circle circumference by the number of teeth (z).
p = πd / z
However, this pitch includes the pi, π(3.1415....) is included, which makes the calculation complicated.
Therefore, the pitch is divided by π (omitting π) to give d / z, which is called the module and is used as a unit to express the size of the tooth.
m = d / z
Since the unit of the pitch circle diameter is mm, the unit of the module obtained by dividing the pitch circle diameter by the number of teeth is also mm, but in practice, modules are often used with only a number after the m symbol, such as m1, m2, or m4, instead of adding mm to the module.
As with pitch, the larger the module value, the larger the tooth size.

Image 2 - Size comparison of Module 0.8 teeth (left) and Module 2 teeth (right)
The JIS standard defines the standard module values (Table 1) for spur and helical gears for general and heavy machinery, and recommends the use of row I as much as possible and the avoidance of module 6.5 as much as possible.
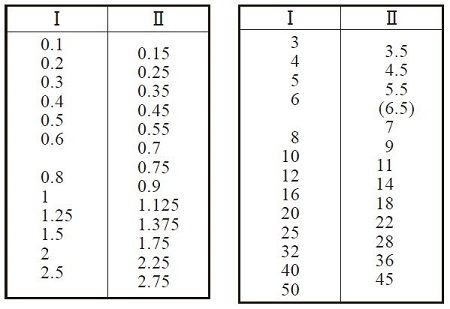
Table 1 - Standard values of module (unit mm)
As mentioned above, ISO specifies the module as a unit to express the size of gear teeth, but in practice, the DP (diametral pitch) is often used in the United States and other countries that use the inch as a unit of length, and sometimes the circular pitch (CP) is also used.
(By making this circular pitch a whole number, it is easy to make the feed distance in the feed mechanism a perfect whole number)
The chart shown in Table 2 compares the equivalent values of module (m), circular pitch (CP) and diametral pitch (DP).
| Module m |
Pitch CP |
Diametral Pitch DP |
|---|---|---|
| 0.39688 | 1.24682 | 64 |
| 0.5 | 1.57080 | 50.8 |
| 0.52917 | 1.66243 | 48 |
| 0.6 | 1.88496 | 42.33333 |
| 0.79375 | 2.49364 | 32 |
| 0.79577 | 2.5 | 31.91858 |
| 0.8 | 2.51327 | 31.75 |
| 1 | 3.14159 | 25.4 |
| 1.05833 | 3.32485 | 24 |
| 1.25 | 3.92699 | 20.32 |
| 1.27000 | 3.98982 | 20 |
| 1.5 | 4.71239 | 16.93333 |
| 1.59155 | 5 | 15.95929 |
| 1.58750 | 4.98728 | 16 |
| 2 | 6.28319 | 12.70 |
| 2.11667 | 6.64970 | 12 |
| 2.5 | 7.85398 | 10.16 |
| 2.54000 | 7.97965 | 10 |
| 3 | 9.42478 | 8.46667 |
| 3.17500 | 9.97456 | 8 |
| 3.18310 | 10 | 7.97965 |
| 4 | 12.56637 | 6.35 |
| 4.23333 | 13.29941 | 6 |
| 4.77465 | 15 | 5.31976 |
| 5 | 15.70796 | 5.08 |
| 5.08000 | 15.95929 | 5 |
| 6 | 18.84956 | 4.23333 |
| 6.35000 | 19.94911 | 4 |
| 6.36620 | 20 | 3.98982 |
| 8 | 25.13274 | 3.175 |
| 8.46667 | 26.59882 | 3 |
| 10 | 31.41593 | 2.54 |
Table 2 - Comparison of various pitch measurements
What are transverse and normal modules?
There are two types of tooth profiles for helical gears and worm gears, the transverse type and the normal type, depending on the reference cross section of the tooth profile.
A module in the transverse plane, where the reference cross section of the tooth profile is perpendicular to the central axis of the gear, is called a transverse module (axial module).
On the other hand, a module in the normal plane, where the reference cross section of the tooth profile is perpendicular to the tooth trace, is called a normal module. For manufacturing reasons, most helical gears currently manufactured are of the normal type.
When meshing a pair of gears, even if they have the same helix angle and module value, they will not mesh correctly if the types of tooth profiles mentioned above are different.
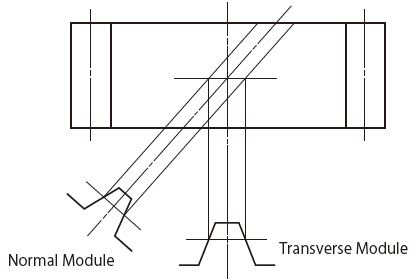
Transverse Module and Normal Module
Related links :
齿轮模数
模数0.5的齿轮
模数1的齿轮
模数1.5的齿轮
模数2的齿轮
模数2.5的齿轮
模数3的齿轮
模数5的齿轮



